Energy Efficient Windows
A condensing boiler can save up to 30% on your heating bills
All properties lose heat through their windows. But energy-efficient glazing keeps your home warmer and quieter as well as reducing your energy bills. That might mean secondary glazing, double-glazing or even triple-glazing.
BENEFITS OF ENERGY-EFFICIENT WINDOWS
Reduce your energy bills.
Reduce your carbon footprint.
More comfortable home: energy-efficient glazing reduces heat loss through windows and means fewer draughts and cold spots.
Peace and quiet: as well as keeping the heat in, energy efficient-windows insulate your home against external noise.
Reduced condensation: energy-efficient glazing reduces condensation build-up on the inside of windows.
The costs and savings for energy-efficient glazing will be different for each home and each window, depending on its size, material and the installer you choose. Good quality double glazing should last for 20 – 30 years or longer
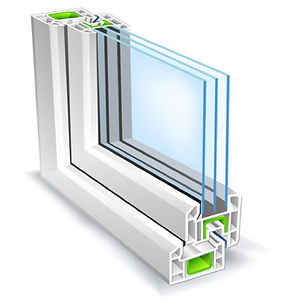
HOW ENERGY-EFFICIENT GLAZING WORKS
Double-glazed windows have two sheets of glass with a gap in between (modern double glazing has a gap of approximately 16mm), to create an insulating barrier that keeps heat in. This is sometimes filled with gas. Triple-glazed windows have three sheets of glass, which are generally more energy efficient, albeit at a greater price.Energy-efficient windows come in a range of frame materials and styles. Performance criteria vary according to the following:
How well they stop heat from passing through the window.
How much sunlight travels through the glass.
How little air can leak in or out around the window.
WHAT TO LOOK FOR
Glass : The most energy-efficient type for double glazing is low emissivity (Low-E) glass. This often has an invisible coating of metal oxide, normally on one of the internal panes. This lets in light and heat but cuts the amount of heat that can get out.
Gaps between the glass: Very efficient windows might use gases such as argon, xenon or krypton in the gap between the sheets of glass.
Pane spacers: These are set around the inside edges to keep the two panes of glass apart. For maximum efficiency, look for pane spacers containing little or no metal – often known as ‘warm edge’ spacers.
FRAME MATERIALS
For all frame materials there are windows available in all energy ratings.
uPVC frames last a long time and may be recycled.
Wooden frames can have a lower environmental impact, but require maintenance. They are often used in conservation areas where the original windows had timber frames.
Aluminium or steel frames are slim and long-lasting, and may be recycled.
Composite frames have an inner timber frame covered with aluminium or plastic. This reduces the need for maintenance and keeps the frame weatherproof.
ENERGY RATING
Some window manufacturers show the energy efficiency of their products using an energy-rating scale from A to G. The whole window (the frame and the glass) is assessed on its efficiency at retaining heat. The scheme is run by the British Fenestration Rating Council (BFRC).
U-VALUES
Windows that have an energy rating will have the u-value of the window displayed on the energy label. A u-value is a measure of how easily heat can pass through a material. Materials that let out more heat have higher u-values whereas materials that let less heat pass through them have lower u-values.
In some cases, windows with a higher energy performance rating might have a higher u-value than windows with a better energy efficiency rating. This might seem the wrong way round as lower u-values indicate better insulation levels. However, in these cases it will be that there are other aspects of the window that make them better overall such as coating used on the glass and the gap between the glass panes.
VENTILATION
Replacement windows will be more airtight than your original frames, so condensation may build up in your house due to the reduced ventilation. If your house does not have much background ventilation, look for replacement windows with trickle vents incorporated into the frame to let in a controlled amount of ventilation.
If you start to see condensation building up around your windows, there may be a damp problem in your home. As a general rule, damp occurs when there is inadequate ventilation, inadequate heating, inadequate insulation or a combination of these. If you’ve started to notice condensation in between the panes of glass in your double-glazing units then it is likely that the seal is broken, and the unit will need to be replaced.
CONSERVATION AREAS
These areas are of special architectural or historic interest, meaning that any work you carry out on your home must preserve or enhance the character of the area. This does not necessarily mean you cannot replace your windows, but might mean you will need to get windows that complement the character of the building and area. Double glazing can be made to look like your building’s original windows, but for any changes you do need to contact your local council’s conservation officer for guidance.
WINDOWS IN PERIOD PROPERTIES
If you live in a conservation area or in a listed building there may be restrictions on what you can do to your windows. There are a number of non-intrusive window insulation options available for historic homes such as heavy lined curtains, shutters, secondary glazing and sealed blinds. However, each historic building is considered individually so check with your local council to see what options are available to you.
LISTED BUILDINGS
Listed buildings have tight controls on what you can change on the outside and sometimes the inside as well, depending on their grading. Old sash windows in historic properties can be protected not only for their appearance but also the materials and methods used to make them. But secondary glazing can be a non-intrusive way of insulated historic windows from the inside, and may be granted permission.
There are other ways to make historic buildings more energy efficient but you will need to consult, and apply for permission from, your local planning authority.
SASH WINDOWS
Sash window units are common features of period properties and can be a design feature. They consist of two vertically sliding frames, but are often badly fitting and made of single pane glass so have poor insulating properties.
If you want to insulate your sash windows there are a number of alternatives to conventional double glazing. If you want to keep the design and look of the sash windows, there are units available that are in keeping with the original design; these are fitted and sealed to prevent draughts and incorporate double glazing to reduce heat loss. The frames don’t need to be plastic, but can be metal or wood with an insulated core.
An increasing number of double glazing companies offer double glazing in period properties. Replacing sash windows can be expensive, so good-quality secondary glazing may be worth considering.
ALTERNATIVES TO DOUBLE GLAZING
If you can’t install double glazing – for example, if you live in a conservation area, period property, or listed building – you can install secondary glazing, or use heavy curtains, or do both.
SECONDARY GLAZING
A secondary pane of glass and frame can be fitted inside the existing window reveal. This won’t be as well sealed as a double-glazing unit, but will be much cheaper to fit, and will still save energy. Low emissivity glass will improve the performance of secondary glazing.
CURTAINS, SEALED BLINDS AND SHUTTERS
Curtains lined with a layer of heavy material can reduce heat loss from a room through the window at night and cut draughts. Hollow blinds, fitted into place with a sealed frame, and sealed shutters will also help cut draughts and keep your heat in for longer.
Check Your Eligibility Using Our Grant Checker
Please ensure that all information provided below is 100% accurate. Any errors in your personal information could delay or prevent you qualifying for a government funded grant
Please note that you do not necessarily need to be in receipt of tax credits or benefits as we still may be able to obtain funding for you via your Council or through other funding schemes.